
CIS105: Computer Applications & Information Systems Lect. 3
Author:Anda Toshiki
Updated:a day ago
Words:582
Reading:3 min
Chapter 3: Computer Hardware
3.1: Technical Terminologies
- System Unit: Main body of the computer that contains a motherboard.
- Motherboard (AKA Circuit Board): Main component of a system unit; a compleex array of electronics that connect and help different components of the computer communicate with each other.
- PC: Motherboards, Mac; Logic Boards
- Chassis (AKA Case or Box): Case to enclose the main components of a computer
- Microprocessor: The brains of the computer
- Central processing unit (CPU): Interprets program instructions and processes data by performing arithmetic and logical operations.
3.2: Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Speed is directly, but not solely, related to the CPU
- Measured in Clock Rate
- The number of cycles per second, that a computer can perform its most basic task
- RSIC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer): Many chips encased into one chip
- Bus Lines; Pathways that transfer data and power between components inside of a computer.
| Architecture Diagram of CPU | Actual CPU Image |
|---|---|
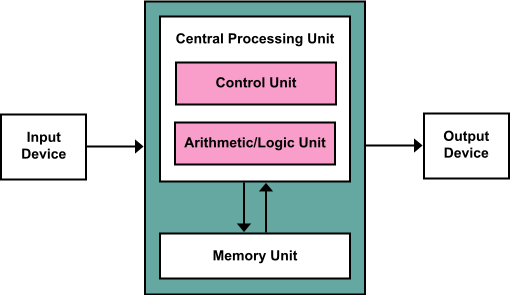 |
3.3 Power Supply Unit (PSU)
- Supplies electricity
- Converts 100-120 volts or 220-240 volts of alternating current (AC) to a lower voltage direct current (DC) that can be used by the internal components of the system unit
- Different currents used in different parts of the world.
3.4: Primary and Secondary Storage
- Primary: The workbench
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Primary storage
- Secondary: The storage for all your tools and supplies
- Hard Drive: Secondary storage
- ROM Chips (Read-Only Memory): Preprogrammed chips that serve specialized internal tasks. No human intervention
- AKA Firmware
3.4.1: Secondary Storage Contd.
- Internal vs. External Storage
- Hard Drivers vs. Solid State Drivers (SSDs)
- Impractical for a computer to be stand-alone
- Important to consider business needs
- Bad IT can make or break a business
3.5: Binary Number System
Computer only understands one language: Machine code or machine language
1 or 0 (on or off)
1s or 0s are referred to as bits (short for binary digits)
8 bits become a byte
- Byte 8 bits
- Kilob
American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII): The coding scheme that most microcomputer use to represent bytes.
Name Equal To Size (In Bytes) Bit 1 Bit 1/8 Nibble 4 Bits 1/2 (rare) Byte 8 Bits 1 Kilobyte 1024 Bytes 1024 Megabyte 1, 024 Kilobytes 1, 048, 576 Gigabyte 1, 024 Megabytes 1, 073, 741, 824 Terrabyte 1, 024 Gigabytes 1, 099, 511, 627, 776 Petabyte 1, 024 Terabytes 1, 125, 899, 906, 842, 624 Exabyte 1, 024 Petabytes 1, 152, 921, 504, 606, 846, 976 Zettabyte 1, 024 Exabytes 1, 180, 591, 620, 717, 411, 303, 424 Yottabyte 1, 024 Zettabytes 1, 208, 925, 819, 614, 629, 174, 706, 176
3.6: Peripheral Devices
- Input v. Output
- Input device: keywords, mice, touchpad, stylus, speakers, microphone, digital camera, etc/
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Converting printed text to digital text
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID): An input mechanism that can be used to label a product for identification and have the product's information transmitted through radio waves.
3.7: Output Devices Contd.
- Monitor: A series of transistors that translate machine code into text and images./
- Pixels: A single dot on a graphic or text image
- Resolution: The number of pixels inside a defined dimension on a monitor, commonly referred to as dots per inch (dpi).
- Resolution is the most important feature of a monitor.
 Toshiki's Note
Toshiki's Note